
In today’s tech-driven world, companies rely on digital systems, making data center services crucial. These centers form the backbone of our digital economy, letting businesses across sectors store, process, and handle data and information without a hitch. From top-notch security to cutting-edge management tools, data center providers in India are changing their approach to keep up with new needs.
Going digital doesn’t just boost economic growth in all industries. It also paves the way for better public services more social and financial inclusion higher productivity, and a more connected society. Experts predict India’s digital economy will hit about $1 trillion by 2025. The government has helped improve the business environment for data center operators and developers. They’ve done this by giving data centers infrastructure status and introducing the Draft Data Centre Policy in 2020.
Let’s take a closer look at what data center services involve, check out the top providers in India, and see how they play a key role in the digital world.

What Are Data Center Services?
Data center services cover a wide range of solutions to ensure smooth operation, protection, and oversight of data center infrastructure. These services include:
1. Colocation:
- Allows companies to lease physical space in a data center for their IT equipment.
- Provides flexibility and lets businesses control their hardware and software.
- Makes sense for organizations that need critical hardware or have high-security needs
2. Managed Services:
- It involves hiring outside help to take care of IT infrastructure upkeep.
- Covers things like looking after servers, managing networks, and keeping an eye on security.
- It helps cut down on running costs and frees up other resources within a company.
3. Cloud Services:
- Provide computing resources like storage and processing power through the internet
- Scalable and flexible to adapt dynamic needs.
- Includes Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
4. Cybersecurity Solutions:
• Protection against cyber threats – hacking, malware, ransomware
• Firewall protection, intrusion detection, and data encryption features
• Play a key role in keeping sensitive information safe and businesses running
5. Network Connectivity:
• Ensure the transferring of data without failure at all times waste. High-speed network connections.
• Dedicated internet access, MPLS network, and SD-WAN solutions.
• Essentially, it is necessary for businesses with remote offices or global operations.
In India, adopting technologies like IoT, AI, and big data analytics has increased the demand for these services. Businesses require robust and scalable infrastructure. In such a situation, the role of companies involved in data center management is a must.
Data Center Services in India: An Overview
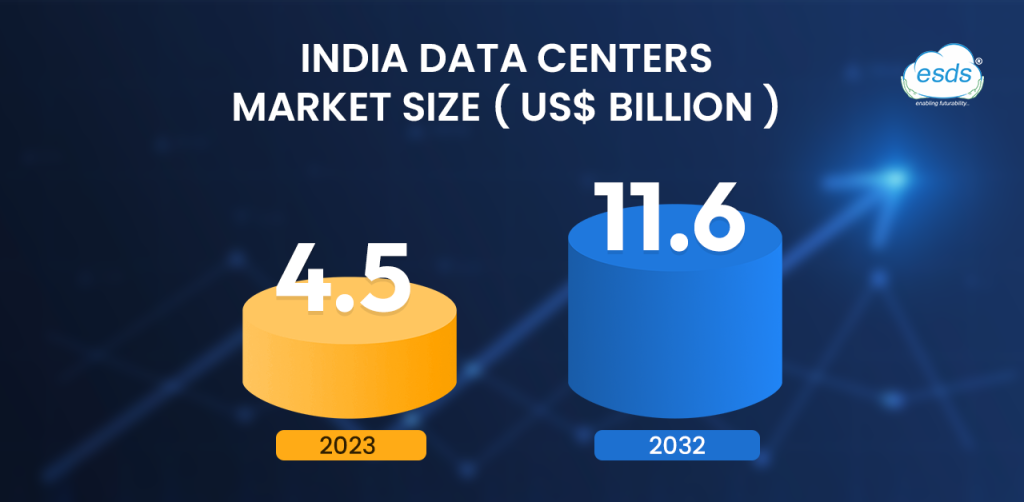
Data centers are booming worldwide, even with some challenges. India stands out in the APAC region, with the biggest data center capacity of about 950 MW. This beats major countries like Australia, Hong Kong SAR, Japan, Singapore, and Korea, as a CBRE report shows.
India’s set to grow the most in the region, adding around 850 MW from 2024 to 2026. This boom highlights India’s strong points in the data center field. For instance, low-cost land, skilled workers, good transport, and a steady power supply are drawing big investments from tech leaders. Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are building massive data centers in the country. India has become a global hotspot for data center services. Many companies are putting money into top-notch infrastructure. The country’s helpful policies, which allow more people to use the internet, and a growing digital economy are pushing this sector forward.
Key Features of Data Center Services in India:
- Cost Efficiency: Affordable solutions tailored to meet diverse business needs.
- Strategic Locations: Data centers located in regions with low latency and high connectivity.
- Green Initiatives: energy-efficient technology adoption to reduce carbon footprint.
- Compliance and Standards: Observance of international standards such as ISO 27001 and GDPR.
Top Data Center Management Companies in India
There are numerous data center management companies in India offering top-notch services. The companies ensure the facilities are operational, minimize downtime, and deliver maximized performance.
The best among them is:
- ESDS: A Pioneer in the Indian Data Centre Industry, ESDS offers a one-stop-shop solution for cloud, IT security, and managed services. With security and reliability as top priorities, ESDS enables businesses to undergo digital transformation.
- CtrlS: CtrlS stands for world-class data centers at global standards and offers excellent colocation and managed services.
- Sify Technologies: Sify is also an Indian provider of data center and network services that offer cloud computing, cybersecurity, and disaster recovery, among several other solutions.
- Yotta: Yotta is India’s leading data center and cloud services provider that offers managed services, cybersecurity, and disaster recovery.
- Web Werks: One of the most influential players in the Indian data center market, offering reliable and scalable colocation and cloud services.
Importance of Data Center Security
With the rise in cyber threats, ensuring the security of data centers has become paramount. Data breaches can lead to severe financial and reputational damage, making security a top priority for service providers.
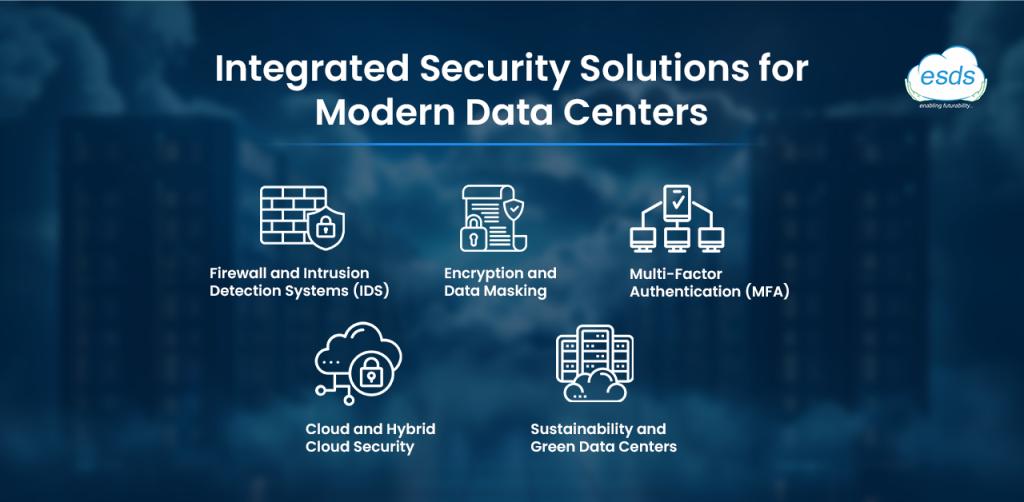
Key Components of Data Center Security:
- Physical Security: biometric access controls, surveillance cameras, and secure perimeters.
- Cybersecurity Measures: firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular vulnerability assessments.
- Data encryption: protecting data both in transit and at rest.
- Disaster Recovery Plans: Ensuring business continuity in case of disruptions.
Data center security involves protecting physical assets, safeguarding critical business information, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Data Center Servers and Their Role
Servers form the core of any data center. They process data , store applications , and manage the network traffic.
Advanced, high-powered data centers deploy advanced servers with cutting-edge processors, large amounts of storage, and efficient cooling to handle growing workloads.
Benefits of Advanced Data Center Servers:
- High Performance: Faster data processing and reduced latency.
- Scalability: ability to handle growing data volumes.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduced operational costs through optimized power usage.
- Reliability: minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operations.

The Future of Data Center Services in India
With the help of future technologies combined with more digital adoption, the prospects of the data center service in India seem bright. The key trends influencing the data center industry are:
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source to reduce latency.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Leveraging AI and ML to optimize data center operations.
- Sustainability: Pursuing green practices to minimize environmental footprint.
- 5G and IoT: supporting the growth of connected devices and real-time applications.
Conclusion
While data centers will remain a concentrated industry in tier-I locations, the market has observed a significant move, with most colocation and edge computing facilities entering tier-II and tier-3 cities. The understanding behind this expansion is to be closer to their customers, provide faster response times, lower latency for applications requiring it, and decentralize DC infrastructure to effectively cover a distributed user base in India.
Cities such as Kochi, Jaipur, Ahmedabad, Lucknow, Patna, and Vishakhapatnam are emerging due to their strategic positioning and better infrastructure, particularly in power supply and improvements in fiber and cable connectivity.
The Indian data center sector is likely to witness significant growth over the next couple of years, with increasing stakeholder focus on Tier II and III cities, sustained occupier interest, a growing talent base, and the strengths of the country as a hub for technology, R&D, and shared service platforms. This will help boost capacity expansion in the country and increase India’s standing as one of the world’s premier global hubs for data centers, a place for innovation, and a potential source of huge international investment.
The rise of the digital economy has made the role of the data center even more crucial.
Data centers’ task at hand is to ensure safe security and innovative management solutions, and Indian service providers have been on the leading edge of this change. Companies like ESDS are first in line with advanced infrastructure, a customer-centric approach, and a sustainable commitment.
Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, you should take your success with reliable data center services in today’s digital-first world. You can, therefore, be sure that your data management needs are in good hands with ESDS as your partner.








Recent Comments